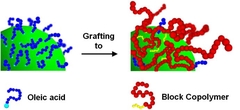
Quantum Dot-Block Copolymer Hybrids with Improves Properties and Their Application to Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Devices
M. Zorn, W.K. Bae, J. Kwak, H. Lee, C. Lee, R. Zentel, K. Char, ACS Nano 2009, 3 (5), 1063-1068.
DOI: 10.1021/nn800790s
To combine the optical properties of CdSe@ZnS quantum dots (QDs) with the electrical properties of semiconducting polymers, we prepared QD/polymer hybrids by grafting a block copolymer (BCP) containing thiol anchoring moieties poly(para-methyl triphenylamine-b-cysteamine acrylamide) onto the surfaces of QDs through the ligand exchange procedure. The prepared QD/polymer hybrids possess improved processability such as enhanced solubility in various organic solvents as well as the film formation properties along with the improved colloidal stability derived from the grafted polymer shells. We also demonstrated light-emitting diodes based on the QD/polymer hybrids, exhibiting the improved device performance (i.e., 3 fold increase in the external quantum efficiency) compared with the devices prepared by pristine (unmodified) QDs.
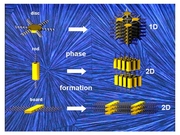
Liquid Crystalline Ordering and Charge Transport in Semiconducting Materials
W. Pisula, M. Zorn, J.Y. Chang, K. Müllen, R. Zentel, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 1179-1202.
DOI: 10.1002/marc.200900251
Liquid crystalline ordering offers the possibility of improving charge carrier mobility. This review discusses the potential of LC-mediated ordering of rod- and disc-like objects in pure organic and organic-inorganic hybrid structures.

Characterization of Quantum Dot/Conducting Polymer Hybrid Films and Their Application to Light-Emitting Diodes
J. Kwak, W. K. Bae, M. Zorn, H. Woo, H. Yoon, J. Lim, S. W. Kang, S. Weber, H.-J. Butt, R. Zentel, S. Lee, K. Char, C. Lee, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1-5.
DOI 10.1002/adma. 200902072
Quantum dot/conducting polymer hybrid films are used to prepare light-emitting diodes (LEDs). The hybrid films (CdSe@ZnS quantum dots excellently dispersed in a conducting polymer matrix, see figure) are readily prepared by various solution-based processes and are also easily micropatterned. The LEDs exhibit a turn-on voltage of 4 V, an external quantum efficiency greater than 1.5%, and almost pure-green quantum-dot electroluminescence.
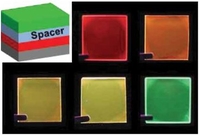
Tunable phosphorescent emission through energy transfer within multilayer thin films based on a carbazole-based host and Ir(III)-complex guest system
H. Kim, Y.-Y. Lyu, K. Choi, R. Zentel, S.-H. Lee, K. Char, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 1232 -1237.
DOI: 10.1002/marc.200900023
Tunable phosphorescent emission properties such as intensity and color are realized by control of energy transfer between different colored Ir(III)-complexes and a carbazole-based host material in multilayer thin films prepared by the spin-assisted layer-by-layer method. The fine tuning of emission properties is achieved by adding a non-emitting spacer layer between the Ir(III)-complex and host material of nanometer range.
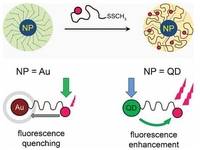
Hetero-telechelic dye-labeled polymer for nanoparticle decoration
P. J. Roth, K.-S. Kim, S. H. Bae, B.-H. Sohn, P. Theato, R. Zentel*, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 1274 -1278.
DOI: 10.1002/marc.200900254
A PMMA with a methyl disulfide and a fluorescent dye end group, synthesized by the RAFT process was used to functionalize the surfaces of gold nanoparticles and of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. The fluorescence of the dye was quenched when tethered to gold nanoparticles, while quantum dots caused an increased dye emission.
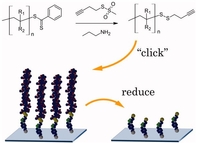
Versatile ω-end group functionalization of RAFT polymers using functional methane thiosulfonate
P.J. Roth, D. Kessler, R. Zentel, P. Theato, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2009, 47 , 3118-3130.
DOI: 10.1002/pola.23392
The high and selective reactivity of methane thiosulfonates toward thiols can be used to intercept terminal thiols generated in situ from polymers prepared by the RAFT process through aminolysis. Thereby, side reactions such as oxidation forming polymer-polymer disulfides or backbiting forming terminal thiolactons on poly[(meth)acrylates] are avoided. By employing a functionalized methane thiosulfonate, we could introduce a terminal triple bond connected with a disulfide bridge with near quantitative yields into various polymethacrylates, polystyrene and poly[N-isopropylacrylamide]. The acetylene-terminated polymers were clicked onto an azide functionalized surface and were removed again by selective reduction of the disulfides.
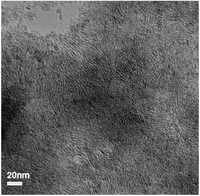
Synthesis, characterization and hierarchical organization of tungsten oxide nanorods: spreading driven by marangoni flow
A. Yella, M.N. Tahir, S. Meuer, R. Zentel, R. Berger, M. Panthöfer, W. Tremel, J. Am. Chem. Soc 2009, 131 (48), 17566–17575.
DOI: 10.1021/ja9007479
Tungsten oxide nanorods were synthesized by a soft chemistry approach using tungsten alkoxide and trioctyl amine and oleic acid as the surfactants. The optical properties of the nanorods were studied. The nanorods were found to be soluble in a wide range of solvents like chloroform, cyclohexane, and so on. Upon solvent evaporation, the nanorods formed hierarchically organized solid state structures. Depending on the solvent used, the nanorods organized in different mesostructures. Moreover, the organization of the nanorods from mixtures of polar and nonpolar solvents was studied. Here, the Marangoni effect resulting from differences in the surface tensions of the two solvents was found to play a role in the organization of the nanorods. Furthermore, dip coating of the nanorod solutions on a mica substrate resulted in the formation of a uniform thin film of the nanorods, which may be useful for a variety of applications such as in electrochromic devices and in organic light emitting devices (OLEDs) using tungsten oxide as a buffer layer.
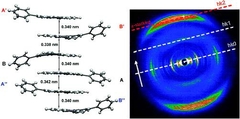
Controllable Columnar Organization of Positively Charged Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Choice of Counterions
Dongqing Wu, Wojciech Pisula, Volker Enkelmann, Xinliang Feng, Klaus Müllen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131 (28), 9620–9621.
DOI: 10.1021/ja902420u
A novel columnar organization of ionic complexes based on 9-phenylbenzo[1,2]quinolizino[3,4,5,6-fed]phenanthridinylium (PQP) has been achieved via ionic self-assembly. These complexes represent the first family of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons containing a large charged aromatic core with controllable columnar organization in both the crystalline and liquid-crystalline phases. The single-crystal structure of the ionic complex with a benzenesulfonate anion exhibits a staggered dimer arrangement of PQP cations that further establishes columnar superstructures. The use of sulfonate anions with long alkyl tails leads to well-ordered discotic columnar mesophases with an identical staggered packing of the PQP cations.
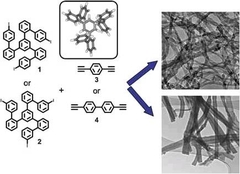
Synthesis of Microporous Carbon Nanofibers and Nanotubes from Conjugated Polymer Network and Evaluation in Electrochemical Capacitor
Xinliang Feng, Yanyu Liang, Linjie Zhi, Arne Thomas, Dongqing Wu, Ingo Lieberwirth, Ute Kolb, Klaus Müllen, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2125-2129.
DOI: 10.1002/adfm.200900264
1D fibers and tubes are constructed through the oriented carbon-carbon crosslinking reactions towards rigid conjugated polymer networks. As the result, a template-free and one-step synthesis of CNTs and CNFs are achieved through a simple carbonization of the as-formed carbon-rich tubular and fiberlike polyphenylene precursors under argon. Microporous CNTs and CNFs with a surface area up to 900 m2 g-1 are obtained.
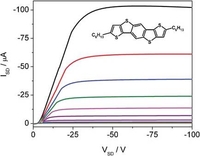
Diethieno(2,3-d;2',3'-d')benzo(1,2,-b;4,5-b')dithiophene (DTBDT) as Semiconductor for High-Performance, Solution-Processed Organic Field-Effect Transistors
Peng Gao, Dirk Beckmann, Hoi Nok Tsao, Xinliang Feng, Volker Enkelmann, Martin Baumgarten, Wojciech Pisula, Klaus Müllen, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 213-216.
DOI: 10.1002/adma.200802031
The facile synthesis of a new five-ring-fused pentacene analog with four symmetrically fused thiophene ring units (Dithieno[2,3-d;2 ,3 -d ]benzo[1,2-b;4,5-b ]dithiophene, Cn-DTBDT) is presented. After aligning this material from solution, thin films for organic field-effect transistors were obtained, resulting in excellent hole mobilities of up to 1.7 cm2V-1s-1, and on/off ratio of 107.
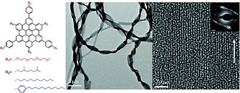
Controlled Self-Assembly of C3-Symmetric Hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronenes with Alternating Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Substituents in Solution, in the Bulk, and on a Surface
Xinliang Feng, Wojciech Pisula, Tibor Kudernac, Dongqing Wu, Linjie Zhi, Steven De Feyter, Klaus Müllen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131 (12), 4439–4448.
DOI: 10.1021/ja808979t
In this work, we introduce a class of C3-symmetric hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronenes (HBCs) 1 with alternating hydrophilic and hydrophobic substituents to achieve control over the self-assembly of discotic nanographene molecules. Our studies show that the following structural parameters and experimental conditions are essential for tailoring the formation of the liquid-crystalline phase in the bulk as well as the self-assembly in solution and on surfaces: (1) steric demand of alkyl and alkylphenyl substituents; (2) noncovalent hydrophilic−hydrophobic interactions of the substituents; and (3) processing conditions, such as the type and mixture of solvents of different polarities along with the nature of the surface. The substitution of HBC with linear alkyl side chains possessing less steric demand (1b) leads to high crystallinity in the bulk solid state and at the liquid−solid interface, and the additional feature of alternating hydrophilic and hydrophobic substituents promotes a high aggregation tendency in polar/apolar solvent mixtures. In contrast, bulky branched alkyl chains (1a) and alkylphenyl substituents (1c) induce liquid crystallinity over the whole temperature range measured. While 1a does not show pronounced self-assembly in solution, compound 1c displays, even at high temperatures, aggregation in polar/apolar solution due to the intermolecular “locking” of peripheral phenyl groups. After solution deposition on a surface, distinct fiber formation is observed for the HBC derivatives, which is related to the solution self-assembly behavior. The present work provides further insight into the molecular design and self-assembly of discotic nanographene materials.
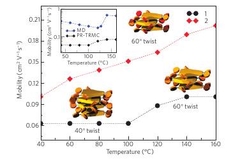
Towards high charge-carrier mobilities by rational design of the shape and periphery of discotics
Xinliang Feng, Valentina Marcon, Wojciech Pisula, Michael Ryan Hansen, James Kirkpatrick, Ferdinand Grozema, Denis Andrienko, Kurt Kremer, Klaus Müllen, Nature Materials 2009, 8, 421-426.
DOI:10.1038/nmat2427
The best discotic liquid crystals so far are built around the coronene unit and possess six-fold symmetry. In the discotic phase their molecules stack with an average twist of 30◦, whereas the angle that would lead to the greatest electronic coupling is 60◦ . Here, a molecule with three-fold symmetry and alternating hydrophilic/hydrophobic side chains is synthesized and X-ray scattering is used to prove the formation of the desired helical microstructure. Time-resolved microwave-conductivity measurements show that the material has indeed a very high mobility, 0.2 cm2 V−1 s−1. The assembliesof molecules are simulated using molecular dynamics, confirming the model deduced from X-ray scattering. The simulated structures, together with quantum-chemical techniques, prove that mobility is still limited by structural defects and that a defect-free assembly could lead to mobilities in excess of 10 cm2 V−1 s−1 .

Controlling the Charge Transfer in Phenylene-Bridged Borylene−Amine π-Conjugated Systems
Agnieszka Pron, Gang Zhou, Hassan Norouzi-Arasi, Martin Baumgarten, Klaus Müllen, Org. Lett. 2009, 11 (16), 3550–3553.
DOI: 10.1021/ol9012487
Novel boron−nitrogen-containing π-conjugated compounds 3,3′- and 4,4′-((2,4,6-triisopropylphenyl)borylene)bis(N,N-diarylbenzenamine) (1−2), m- and p-phenylene bridged to the boron center, respectively, have been synthesized and characterized. Optical studies by means of UV−vis absorption and emission measurements as well as DFT calculations reveal a different charge transfer behavior between the para series and the meta series at ground and excited states.
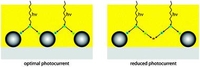
Exciton diffusion controlled quantum efficiency in hybrid dye sensitized solar cells
Zaicheng Sun, Yajun Cheng, Maria Lechmann, Jiaoli Li, Jixue Li, Jishan Wu, Andrew Grimsdale, Klaus Müllen, Hans-Jürgen Butt, Jochen S. Gutmann, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 1604-1609.
DOI: 10.1039/b812217b
We demonstrate that the performance of hybrid organic solar cells depends on the exciton diffusion distance and thus the morphology of the nanoparticles used.
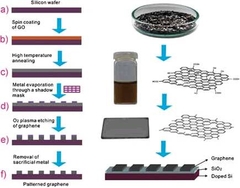
Patterned Graphene Electrodes from Solution-Processed Graphite Oxide Films for Organic Field-Effect Transistors
Shuping Pang, Hoi Nok Tsao, Xinliang Feng, Klaus Müllen, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21 (34), 3488-3491.
DOI: 10.1002/adma.200803812
A replacement for gold as the hole-injecting metal in organic electronic devices is presented: patterned graphene electrodes prepared from graphite oxide sheets by oxygen plasma etching. Solution-processed organic FETs with poly(3-hexylthiophene) as the semiconductor and these graphene electrodes are shown to perform as well as or even better than devices with gold contacts.
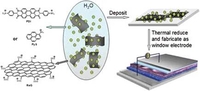
Composites of Graphene with Large Aromatic Molecules
Qi Su, Shuping Pang, Vajiheh Alijani, Chen Li, Xinliang Feng, Klaus Müllen, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21 (31), 3191-3195.
DOI: 10.1002/adma.200803808
A novel approach to functionalize graphene with large aromatic donor and acceptor molecules consisting of nanographene units is presented, producing an unprecedented class of graphene and nanographene composites with tunable electronic properties. The stability of aqueous dispersion of graphene sheets is greatly enhanced, and a large number of monolayer and double-layer graphene sheets could be facilely fabricated on the substrates.
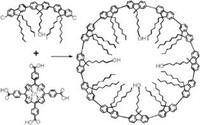
A Macrocyclic Model Dodecamer for Polyfluorenes
Sascha C. Simon, Bruno Schmaltz, Ali Rouhanipour, Hans J. Räder, Klaus Müllen, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21(1), 83-85.
DOI: 10.1002/adma.200802019
A π-conjugated, cyclododeca-2,7-fluorene macrocycle is synthesized as a new model compound for polyfluorenes. The structure formation is demonstrated by 1H NMR spectroscopy, MALDI-TOF, and STM measurements, and the optical properties of this monodisperse cycle are investigated using UV-vis and fluorescence spectroscopy.
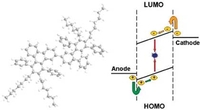
Conjugated Triphenylene Polymers for Blue OLED Devices
Moussa Saleh, Young-Seo Park, Martin Baumgarten, Jang-Joo Kim, Klaus Müllen, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30(14), 1279-1283.
DOI: 10.1002/marc.200900332
Blue-emitting conjugated triphenylene-based polymers have been synthesized using the microwave-assisted Suzuki- Miyaura and Yamamoto polycondensation reactions. All polymers showed deep- blue emission in films with PL maxima around 430 nm. The device performance in terms of luminescence efficiency, power efficiency, turn-on voltage, and electroluminescence present all polymers as good candidates for polymer organic light emitting diodes.
Excitation energy transfer in organic materials: From fundamentals to optoelectronic devices
Frédéric Laquai, Young-Seo Park, Jang-Joo Kim, Thomas Basché, Macrom. Rap. Comm. 2009, 30, 1203-1231.
DOI: 10.1002/marc.200900309
Understanding energy transfer in small organic molecules and conjugated polymers from the single molecule toward the bulk ensemble is a prerequisite for the design of novel materials for organic optoelectronics. Although many energy transfer phenomena in conjugated materials can be approximated by classical Förster- and Dexter-type mechanisms, remains a complete understanding still challenging.
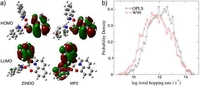
Amorphous films of tris-8(hydroxyquinoline aluminium): force-field morphology and charge transport
Alexander Lukyanov, Christian Lennartz, Denis Andrienko, Physica Status Solidi A 2009, 1-6.
DOI: 10.1002/pssa.200925276
The effect of force-field parameters on the morphology and charge dynamics is assessed for amorphous films of tris(8-hydroxyquinolinato)aluminium. The force-fields OPLS and Williams 99 are used for non-bonded parameters, bonded interactions are calculated from first principles. OPLS describes the morphology better, but the slight differences in molecular packing do not significantly affect charge hopping rates or mobility.
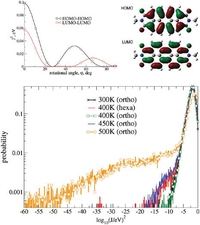
Understanding structure-mobility relations for perylene tetracarboxdiimide derivatives
Valentina Marcon, Wojciech Pisula, Julie Dahl, Dag W. Breiby, James Kirkpatrick, Sameer Patwardhan, Ferdinand Grozema, Denis Andrienko, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11426-11432.
DOI: 10.1021/ja900963v
Discotic mesophases are known for their ability to self-assemble into columnar structures and can serve as semiconducting molecular wires. By combining wide-angle X-ray scattering experiments with molecular dynamics simulations, we elucidate packing motifs of a perylene tetracarboxdiimide derivative. We then relate the charge mobility to the molecular arrangement, both by pulse-radiolysis time-resolved microwave conductivity experiments and simulations based on the non-adiabatic Marcus charge transfer theory. By linking molecular packing and mobility, we eventually provide a pathway to the rational design of perylenediimide derivatives with high charge mobilities.
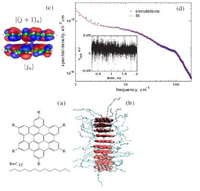
Charge transport in semiconductors with multiscale conformational dynamics
Alessandro Troisi, David L. Cheung, Denis Andrienko, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 116602
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.116602
In partially ordered organic semiconductors, the characteristic times of nuclear motion are comparable to those of charge carrier dynamics. We build a model Hamiltonian which allows the study of charge transport whenever carrier and nuclear dynamics are not easily separable. Performing nanoseconds long molecular dynamics of a columnar mesophase of a discotic liquid crystal and evaluating electronic couplings, we identify realistic parameters of the Hamiltonian. All modes which are coupled to the electron dynamics can be described in the model Hamiltonian by a limited number of Langevin oscillators. This method can be applied to systems with both slow (nanoseconds) and fast (hundreds of femtoseconds) nuclear motions, i.e., with both dynamic and static disorder.
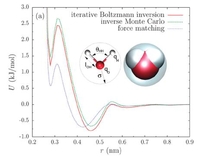
Victor Rühle, Christoph Junghans, Alexander Lukyanov, Kurt Kremer, Denis Andrienko, J. Chem. Theor. Comp. 2009, 5 (12), 3211–3223.
DOI: 10.1021/ct900369w
Coarse-graining is a systematic way of reducing the number of degrees of freedom representing a system of interest. Several coarse-graining techniques have so far been developed, such as iterative Boltzmann inversion, force-matching, and inverse Monte Carlo. We present a versatile object-oriented toolkit for coarse-graining applications (VOTCA) that implements these techniques and provides a flexible modular platform for their further development.
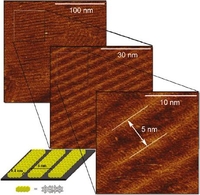
Yulia Fogel, Linjie Zhi, Ali Rouhanipour, Denis Andrienko, Hans Joachim Räder, Klaus Müllen, macromolecules 2009, 42, 6878-6884.
DOI: 10.1021/ma901142g
Anovel homologous series of five monodisperse ribbon-type polyphenylenes, with rigid dibenzo[e,l]pyrene cores in the repeat units, are synthesized by a microwave-assisted Diels-Alder reaction. Their unique structure is especially designed to produce a series of giant ribbon-type polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a single further reaction step by cyclodehydrogenation. These graphitic molecules self-organize into 2D columns when adsorbed on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite, thus rendering them attractive candidates for future applications in organic electronic devices such as e.g. field effect transistors.
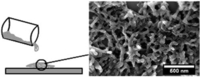
Maria C. Lechmann, Daniel Kessler, Jochen S. Gutmann, Langmuir 2009, 25, 10202-10208.
We demonstrate an integrated approach to prepare a nanostructured, multifunctional material with mutually exclusive, orthogonal properties. The hybrid material was obtained within a single step via self-assembly in solution. It consists of TiO2 as a functional metal oxide and an amphiphilic block copolymer, poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(triphenylamine) (PEO-PTPA). Within the materials' synthesis, the block copolymer not only acts as a templating agent but also adds an electronic functionality to the resulting hybrid material. During the synthesis, a variety of self-assembled morphologies, ranging from spheres to wires, can be created. The obtained morphology depends on the weight fraction of the polymer, solvent, TiO2, and acid (HNO3). When films on silicon wafers are studied with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), a ternary phase diagram could be mapped, whereas the crystallinity of TiO2 could be proved by high-resolution TEM. Different morphologies of this self-assembled hybrid material were tested for solar cell application. Even for devices with layer thicknesses of the active material below 10 nm, power conversion efficiencies up to 0.15% at 1 sun and 1.5 AM were observed.
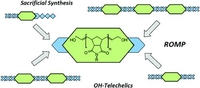
Sacrificial Synthesis of Hydroy-Telechelic Metathesis Polymers via Multiblock-copolymers
S. Hilf, A.F.M. Kilbinger, Macromolecules 2009, 42, 1099-1106.
DOI: 10.1021/ma802440k
The synthesis of well-defined telechelic ring-opening metathesis polymers has been achieved by Sacrificial Synthesis. With the formation of cleavable triblock-copolymers, precise control over the molecular weight and the degree of functionalization was achieved. Introducing cleavable monomers that can be addressed separately, sequential deprotection was accomplished which opened the path to more sophisticated polymeric materials bearing different substituents at their respective chain ends. Sacrificial penta- and heptablock-copolymers are also presented which allow the synthesis of well-defined telechelic polymers in good yields and significantly improved initiator efficiency.
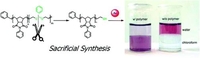
Thiol-functionalized ROMP polymers via Sacrificial Synthesis
S. Hilf, A.F.M. Kilbinger, Macromolecules 2009, 42, 4127-4133.
DOI: 10.1021/ma900036c
The synthesis of well-defined and highly functionalized thiol-functionalized polymers has been accomplished via the ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP). A sacrificial synthesis-based approach was chosen for this interesting functional group since it has proven to give precise control over molecular weight and selective placement of end-groups on a different functionality before. Thiol-functionalized ROMP-polymers were successfully synthesized employing thioacetal monomers, which can be cleaved by hydrogenation leaving the desired thiol group behind. The placement of this highly reactive functional group at one chain end of a poly(norborneneimide) is demonstrated by analytical methods such as MALDI−ToF mass spectroscopy and 1H NMR of derivatized polymers. By kinetic measurements, the functionalization efficiency and the polymerization characteristics of the used dithiepine monomer were determined. In a first demonstration, the coating of gold nanoparticles is shown as one interesting application of such functionalized metathesis polymers.
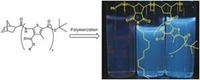
Polymerizable well-defined oligo(thiophenamide)s and their ROMP block-copolymers
S. Hilf, J. Klos, K. Char, H. Woo, A.F.M. Kilbinger, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30, 1249-1257.
DOI: 10.1002/marc200900207.
We report the synthesis of conjugated thiophene amide oligomers that constitute a new class of chromophores with potential for optoelectronic applications. The synthesis of defined norbornene-substituted oligothiophene amides using conventional coupling chemistry is described. Their electronic properties depend on the degree of oligomerization as UV/Vis and fluorescence spectroscopy demonstrate. A significant red shift in the spectra upon an increase in the oligomer length evidences conjugation of the thiophene rings via the amide linkages. ROMP of the norbornene-substituted oligomers gives homopolymers and block-copolymers with a solubilizing second block. The amphiphilic character of the block copolymers is used to study micellization and bulk self-organization.

Ionic Liquids on Demand in Continuous Flow
D. Wilms, J. Klos, A.F.M. Kilbinger, H. Löwe, H. Frey, Org. Process Res. Dev. 2009, 13, 961-964.
DOI: 10.1021/op900069a
We report on the development of an alternative protocol for the facile, solvent-free synthesis of various novel imidazolium-based ionic liquids (ILs) that affords highly pure products without the necessity of subsequent purification steps. The continuous approach is based on the combination of HPLC pumps with a micromixer and a capillary residence tube. Our system provides a high degree of control over the alkylation reactions due to a high surface-to-volume ratio and superior heat and mass transport. Within the scope of our studies, we focused on ionic liquids containing differently substituted phenyl rings and characterized these compounds with respect to further use for direct application or subsequent reaction sequences. Scale-up can conveniently be achieved by operating several reactors with high continuous throughput in parallel.
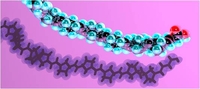
Functional end groups for polymers prepared using the ring-opening metathesis polymerization
S. Hilf, A.F.M. Kilbinger, Nature Chemistry 2009, 1, 537-546.
DOI:10.1038/nchem.347
The precise placement of functional groups on the chain-ends of macromolecules is a major focus of polymer research. Most common living polymerisation techniques offer specific methods of end-functionalisation governed by the active propagating species and the kinetics of the polymerisation reaction. Ring-opening metathesis polymerisation (ROMP) has established itself as one of the most functional group tolerant living polymerisation techniques known but this tolerance has limited the number of available functionalisation reactions. Metathesis chemists have therefore needed to develop a variety of end-functionalisation adapting each of them to the reactivity scheme of the particular catalysts used and the complexity of the group to be attached. This review presents an overview of the methods developed for different types and generations of metathesis catalysts that are typically employed in such polymerisations. We also present a field guide of functionalisation methods highlighting the factors to be considered when choosing the most appropriate approach.
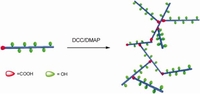
Long-Chain Branched ROMP Polymers
S. Hilf, F. Wurm, A.F.M. Kilbinger, J. Polym. Sci. A 2009, 47, 6932-6940.
DOI: 10.1002/pola.23733
This article describes the construction of branched ROMP-polymer architectures via polycondensation of ABn-type macromonomers. For this convergent strategy, a polymer was synthesized that carries several hydroxyl-groups along the polymer chain and one carboxylic acid group at the chain end. An esterification reaction between these functional groups yielded long-chain branched polymers. The polymers were analyzed by NMR and SEC to monitor the condensation reaction.
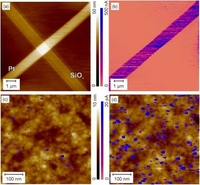
Electrical Modes in Scanning Probe Microscopy
R. Berger, H.-J- Butt, M. Retschke, S. Weber, Macromol. Rapid Comm. 2009, 30, 1167-1178.
DOI: 10.1002/marc.200900220
As molecular electronics advances, the characterization of electrical properties becomes more and more important. Here, we review the major scanning probe microscopy (SPM) modes that are used for electrical characterization of thin films, i.e. scanning conductive force microscopy (SCFM), Kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) and scanning electric field microscopy (EFM). To demonstrate the possibilities and capabilities of these modes, reference sample have been fabricated by means of focused ion beam deposition. Furthermore two upcoming modes are presented which (i) base on local current measurements while the SPM-cantilever is excited into torsional vibrations and (ii) base on changes in a backscattered microwave that was coupled into a SPM-cantilever. The scanning probe based electrical modes are applicable for studies of functional layers used in soft matter electronic devices under realistic environmental conditions.
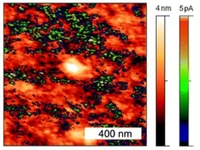
Integrated blocking layers for hybrid organic solar cells
Mine Memesa, Stefan Weber, Sebastian Lenz, Jan Perlich, Rüdiger Berger, Peter Müller-Buschbaum and Jochen S. Gutmann, Energy & Environmental Science 2009, 2, 783-790.
DOI: 10.1039/B902754H
In hybrid organic solar cells a blocking layer between transparent electrode and nanocrystalline titania particles is essential to prevent short-circuiting and current loss through recombination at the electrode interface. Here we report the preparation of a thin, uniform and crack free hybrid blocking layer composed of conducting titania nanoparticles embedded in an insulating polymer derived ceramic. To do so we combine sol–gel chemistry with novel poly(dimethylsiloxane) containing amphiphilic block copolymer, poly(ethyleneglycol) methyl ether methacrylate–block–poly(dimethylsiloxane)–block–poly(ethyleneglycol) methyl ether methacrylate as the templating agent. Conductive probe scanning force microscopy proved that the existing percolating titania networks are separated by an insulating ceramic matrix. The structural uniformity of the percolating structures was investigated by microbeam grazing incidence small angle X-ray scattering making the integrated blocking layer suitable for hybrid organic solar device applications. Preliminary tests with the integrated blocking layer showed reasonable comparison to conventional TiO2 blocking layer containing devices mentioned in the literature.
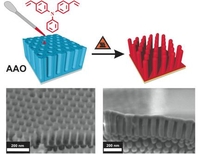
Template-Assisted Fabrication of Free-Standing Nanorod Arrays of a Hole-Conducting Cross-Linked Triphenylamine Derivative: Toward Ordered Bulk-Heterojunction Solar Cells
Niko Haberkorn, Jochen S. Gutmann, Patrick Theato, ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1415-1422.
DOI: 10.1021/nn900207a
Arrays of free-standing nanorod arrays attached to an ITO/glass substrate were fabricated via an anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) template-assisted approach. Aggregation of the nanorod arrays after removal of the template was prevented by applying a freeze drying technique. Due to the large surface area and the electrochemical properties these highly-ordered polymeric replicas have potential application in the field of organic photovoltaics.
Templated Organic and Hybrid Materials for Optoelectronic Applications
Niko Haberkorn, Maria C. Lechmann, Byeong Hyeok Sohn, Kookheon Char, Jochen S. Gutmann, Patrick Theato, Macromol Rapid Comm 2009, 30, 1146-1166.
DOI: 10.1002/marc.200900213
This review compiles different approaches to template organic materials as well as hybrid materials that find application in optoelectronic devices. Two templating approaches are
presented and discussed in detail, e.g. the use of preformed nanoporous membranes as templates for organic materials, and self-assembly processes of materials to pattern hybrid materials. Both routes are very promising templating approaches for optoelectronic materials and represent complementary rather than competing techniques.
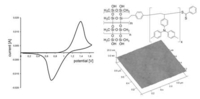
Surface Coatings Based on Polysilsesquioxanes: Solution Processible Smooth Hole-Injection-Layers for Optoelectronic Applications
Kessler, D.; Lechmann, M. C.; Noh, S.; Berger, R.; Lee, C.; Gutmann, J. S.; Theato, P. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2009, 30(14), 1238-1242.
DOI: 10.1002/marc.200900196
Optoelectronic devices usually consist of a transparent conductive oxide (TCO) as one electrode. Interfacial engineering between the TCO electrode and the overlying organic layers is an important method for tuning device performance. We introduce poly(methylsilsesquioxane)-poly(N,N-di-4-methylphenylamino styrene) (PMSSQ-PTPA) as a potential hole-injection layer forming material. Spin-coating and thermally induced crosslinking resulted in an effective planarization of the anode interface. HOMO level (-5.6 eV) and hole mobility (1 × 10-6 cm2 • Vs-1) of the film on ITO substrates were measured by cyclovoltammetry and time-of-flight measurement demonstrating the hole injection capability of the layer. Adhesion and stability for further multilayer built-up could be demonstrated. Contact angle measurements and tape tests after several solvent treatments proved the outstanding film stability.
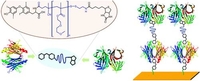
Synthesis of Hetero-Telechelic α,ω Bio-Functionalized Polymers
Peter J. Roth, Florian D. Jochum, Rudolf Zentel and Patrick Theato, Biomacromolecules, 2009, 11, 238-244.
DOI: 10.1021/bm901095j
Reversible addition−fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization was used to synthesize poly[diethylene glycol monomethylether methacrylate] (PDEGMA) (Mn = 6250 g/mol, PDI = 1.14) with a pentafluorophenyl (PFP) activated ester and a dithioester end group. The hormone thyroxin (T4) was quantitatively attached to the PFP activated ester α end group via its amino group. The ω-terminal dithioester was not harmed by this reaction and was subsequently aminolyzed in the presence of N-biotinylaminoethyl methanethiosulfonate, yielding a polymer with a thyroxin and a biotin end group with very high heterotelechelic functionality. The polymer was characterized by 1H, 13C, and 19F NMR, UV−vis, and IR spectroscopy and gel permeation chromatography. The thyroxin transport protein prealbumin with two thyroxin binding sites and streptavidin, which has four biotin binding sites, was conjugated using the biotarget labeled polymer, resulting in the formation of a protein−polymer network, confirming the heterotelechelic nature of the polymer. Polymer−protein microgel formation was observed with dynamic light scattering. To realize a directed protein assembly, prealbumin was immobilized onto a surface, exposing one of its two thyroxin binding groups and thus allowing the conjugation with the thyroxin α end group of the heterotelechelic polymer. The biotin ω end group of the attached polymer layer enabled the subsequent immobilization of streptavidin, yielding a defined multilayer system of two proteins connected with the synthetic polymer (efficiency of streptavidin immobilization 81% based on prealbumin). Without the polymer, no streptavidin immobilization occurred. The layer depositions were monitored by surface plasmon resonance. The synthetic approach of combining PFP activated esters with functional MTS reagents presents a powerful method for obtaining well-defined heterotelechelic (bio-) functionalized polymers.
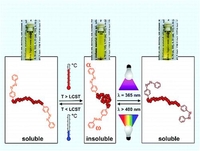
Thermo- and Light-Responsive Polymers Containing Photoswitchable Azobenzene End Groups
Florian D. Jochum, Lisa zur Borg, Peter J. Roth and Patrick Theato, Macromolecules 2009, 42 (20), 7854–7862.
DOI: 10.1021/ma901295f
Telechelic thermo- and light-responsive polymers based on poly(oligo(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate) P(OEGMA) with azobenzene functionalities at the end groups were synthesized. In a reversible addition−fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization using a functionalized chain transfer agent (CTA) containing a pentafluorophenyl (PFP) activated ester, oligo(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate (OEGMA, Mn 300 g mol−1) could successfully be polymerized with good control over molecular weight, very high conversions, and narrow molecular weight distributions. Polymers derived from this CTA possessed an activated ester at the α-end of the polymer chain as well as a dithioester ω-terminus. The ω-dithioester group of each polymer chain could quantitatively be either removed with AIBN treatment or substituted with a PFP ester by using a modified diazo compound. As a consequence, a postmodifiaction of the telechelic reactive end groups was possible through a polymer analogous reaction with amino-functionalized azobenzene. P(OEGMA) polymers containing azobenzene end groups showed a reversible light- and temperature-controlled phase transition in water. Higher values for the lower critical solution temperature (LCST) were measured after irradiation of the aqueous polymer solutions due to the higher polarity of cis-azobenzene. The LCST differences between irradiated and nonirradiated solutions increased linearly upon the ratio of azobenzene units up to 4.3 °C.
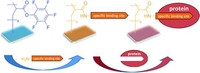
Reactive Surface Coatings Based on Polysilsesquioxanes: Controlled Functionalization for Specific Protein Immobilization
Daniel Kessler, Peter J. Roth, Patrick Theato, Langmuir 2009, 25 (17), 10068–10076.
DOI: 10.1021/la901878h
The key designing in reliable biosensors is the preparation of thin films in which biomolecular functions may be immobilized and addressed in a controlled and reproducible manner. This requires the controlled preparation of specific binding sites on planar surfaces. Poly(methylsilsesquioxane)-poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylates) (PMSSQ-PFPA) are promising materials to produce stable and adherent thin reactive coatings on various substrates. Those reactive surface coatings could be applied onto various materials, for example, gold, polycarbonate (PC), poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (PTFE), and glass. By dipping those substrates in a solution of a desired amine, specific binding sites for protein adsorption could be immobilized on the surface. The versatile strategy allowed the attachment of various linkers, for example, biotin, l-thyroxine, and folic acid. The adsorption processes of streptavidin, pre-albumin, and folate-binding protein were monitored using surface plasmon resonance (SPR), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The presented protein immobilization strategy, consisting of four steps (a) spin-coating of PMSSQ-PFPA hybrid polymer from tetrahydrofuran (THF) solution, (b) annealing at 130 °C for 2 h to induce thermal cross-linking of the PMSSQ part, (c) surface analogues reaction with different amino-functionalized specific binding sites for proteins, and (d) controlled assembly of proteins on the surface, may find various applications in future biosensor design.
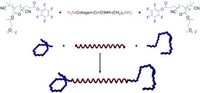
A Versatile Grafting-to Approach for the Bioconjugation of Polymers to Collagen-like Peptides Using an Activated Ester Chain Transfer Agent
Kerstin T. Wiss, Ohm D. Krishna, Peter J. Roth, Kristi L. Kiick, Patrick Theato, Macromolecules 2009, 42 (12), 3860–3863.
DOI: 10.1021/ma900417n
The stimuli-responsive poly(diethylene glycol methyl ether methacrylate) was synthesized via RAFT polymerization using a functional chain transfer agent, which resulted in an activated ester end-group. This well-defined polymer could be conjugated onto the two amine-functionalized chain ends of a collagen-like peptide, which contained an interior Boc-protected lysine. The GPC elugram of the product showed neither diblock formation nor residual homopolymers, indicating the quantitative reaction of the peptide at the chain end of the polymer. Moreover, after deprotection of the peptide, observation by CD spectroscopy clearly indicated that the polymer-b-collagen-b-polymer triblock copolymer showed the triple-helical assembly characteristic of the collagen-like peptide. The triblock copolymers provide new peptide-containing macromolecules in which both block types show stimuli-responsive behavior, which should provide interesting opportunities to modulate self-assembly behavior. This synthetic approach for the site-selective conjugation of RAFT polymers should be broadly applicable for the modification of peptides and polypeptides with well-defined synthetic polymers.