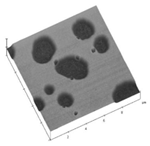
Novel Amphiphilic Styrene-Based Block Copolymers for Induced Surface Reconstruction
Lutz Funk, Martin Brehmer, Huiman Kang, Kookheon Char, Rudolf Zentel, Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics 2008, 209, 52-63. DOI:10.1002/macp.200700312
Fig.: New hydrophilic- hydrophobic blockcopolymers -prepared by NMP mediated living radical polymerization- allow it to study the induced surface reconstitution in detail. The picture shows the break-up of the hydrophobic surface lamella and the up-folding of the hydrophilic lamella in contact with water.
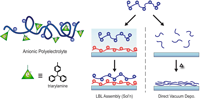
Thin-Films of Poly-Triarylamines for Electro-Optic Applications Kyungsun Choi, Jeonghun Kwak, Changhee Lee, Hosub Kim, Kookheon Char, Dong Young Kim, Rudolf Zentel, Polymer Bulletin 2008, 59, 795-803. DOI:10.1007/s00289-007-0815-4
Fig.: We observed that a new anionic triarylamine copolymer can be used for the preparation of thin semiconducting organic films in two extremely different ways: One is the LBL assembly from solution with a cationic polyelectrolyte as counter system; the other is direct vacuum deposition, whereby the polymer degrades to oligomers, but keeps the functional groups intact. The fabricated films are used in light emitting devices as hole transporting layers showing excellent properties.
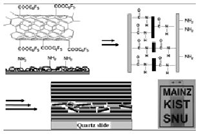
Preparation of Transparent Conductive Multilayered Films Using Active Pentafluorophenyl Ester Modified Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes
Hye Jin Park, Junkyung Kim, Ji Young Chang, Patrick Théato, Langmuir 2008, 24, 10467-10473. DOI:10.1021/la801341t
A mutilayered film was prepared by layer-by-layer (LBL) assembly of active ester modified multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and poly(allylamine hydrochloride) (PAH). For this purpose carboxylic groups on the surface of the oxidized MWCNTs were converted to the acyl chlorides by their reaction with thionyl chloride. Subsequent reaction of the acyl chlorides with pentafluorophenol formed the active esters. These active ester modified MWCNTs (MWCNTs-COOC6F5) were air-stable and moisture resistant, but showed a high reactivity towards primary or secondary amines resulting in amide bonds. For the preparation of a multilayered film, the surface of a quartz slide was first activated and sacrificial double layers of PAH and poly(sodium 4-styrene sulfonate) (PSS) were deposited. Subsequently, LBL assembly of MWCNTs-COOC6F5 and PAH was then conducted on these double layers [(PAH/PSS)2].
In the process of the assembly, a reaction occurred between the active ester on the surface of MWCNTs and the amine groups of polyallylamine yielding amide bonds, which resulted in a mechanically stable thin film. A free-standing film was obtained after dissolving the sacrificial layer [(PAH/PSS)2] in a concentrated aqueous NaOH solution. The surface resistance of the multilayered film with twenty bilayers decreased to around 10 kΩ while remaining a reasonable transparency (70 % at 500 nm).
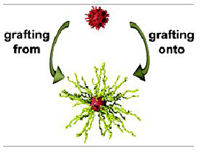
Versatile Synthesis of Functional Gold Nanoparticles: Grafting Polymers From and Onto
Peter J. Roth, Patrick Théato, Chemistry of Materials 2008, 20, 1614-1621. DOI:10.1021/cm702642e
Fig.: Functionalized gold nanoparticles have been prepared in an organic solvent by a two-phase reduction method in ethyl acetate and water using bis-(6-hydroxyhexyl)-disulfide bis-(2-bromoisobutyl)-ester, bis-(6-acetyloxyhexyl)disulfide and bis-(5-carboxypentyl)disulfide bis(pentafluorophenyl)ester as stabilizing ligands. This procedure features the advantages that no phase transfer agent was necessary during the preparation of the gold nanoparticles and that the reducing conditions were mild enough to utilize functional disulfide ligands. The obtained gold nanoparticles with typical sizes between 2 – 5 nm could be precipitated and redispersed without any irreversible aggregation. Using these nanoparticles the stimuli-responsive polymers poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and poly(N-cyclopropylacrylamide) could be grafted from the surface. Also the grafting of polymers onto gold nanoparticles could be demonstrated with amino end-functionalized polyethylenoxide. The reactive character of gold nanoparticles featuring a pentafluorophenyl ester groups on the surface could also be applied in the preparation of multilayers on the basis of covalent bonds between the gold nanoparticles and polyallylamine.
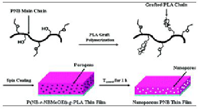
Nanoporous Thin Films Based on Polylactide-Grafted Norbornene Copolymers
Sewon Oh, Jin-Kyu Lee, Patrick Théato, Kookheon Char, Chemistry of Materials 2008, 20, 6974-6984. DOI:10.1021/cm801421w
Fig.: Thermally stable vinyl polymerized polynorbornene (PNB) is one of the challenging materials in porous low dielectric films for packaging applications. Nanoporous PNB thin films were obtained with poly(D,L-lactide) (PLA)-grafted norbornene copolymers. Thermally labile PLA chains act as pore generators in PNB films. Thermally stable PNB main chains were synthesized by Pd-catalyzed vinyl polymerization and PLA side chains were grafted onto the PNB main chains by ring opening polymerization. The brittle and poor processible properties of PNB could easily be controlled by the copolymerization with norbornene derivatives. In thin films, the PLA chains were found to thermally decompose at about 250°C while PNB matrix was stable during this pore generating process. The porosity of the porous PNB thin films could be controlled up to 18% with pore sizes below 5 nm range by varying the chain length of grafted PLA. Introduction of cross-linking epoxy groups onto the PNB main chains resulted in the formation of well-defined nanopores without any extensive pore collapse during the vitrification of the PNB matrix. Additionally, it is also demonstrated that the photo-patterning of the thin films could be achieved by using photoinitiator.
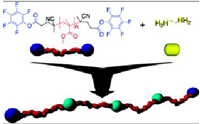
Synthesis of Reactive Telechelic Polymers Based on Pentafluorophenyl Esters
Peter J. Roth, Kerstin T. Wiss, Rudolf Zentel, Patrick Théato, Macromolecules 2008, 41, 8513-8519. DOI:10.1021/ma801681b
Fig.: A diazo initiator and a chain transfer agent (CTA), both containing a pentafluorophenyl (PFP) activated ester, were synthesized. In a RAFT polymerization using the functionalized chain transfer agent (PFP-CTA), methyl methacrylate (MMA), diethyleneglycol monomethylether methacrylate (DEGMA), polyethyleneglycol monomethylether methacrylate (PEGMA) and lauryl methacrylate (LMA) could successfully be polymerized into homopolymers and diblock copolymers with good control over molecular weight. Polymers derived from the PFP-CTA possessed an activated ester at the α-end of the polymer chain. Additionally the pentafluorophenyl ester diazo compound could successfully be employed to functionalize RAFT polymers with a PFP ester at their ω-end. As a consequence, functionalization of both end-groups was possible and led to telechelic polymers, exhibiting an active ester at both ends of the polymer chain.

Synthesis of Reactive Telechelic Polymers Based on Pentafluorophenyl Esters
Peter J. Roth, Kerstin T. Wiss, Rudolf Zentel, Patrick Théato, Macromolecules 2008, 41, 8513-8519. DOI:10.1021/ma801681b
Fig.:In contrast to polystyrene derivatives and poly[(meth)acrylamides], the aminolysis of poly[(meth)acrylates] yields terminal thiolactones by backbiting. These cannot be employed for end group modification or for producing self-assembled monolayers on metal surfaces. We describe the use of methyl methanethiosulfonate during the aminolysis of polymethacrylates which yields well defined methyl disulfide end groups capable of producing stable polymeric self assembled monolayers on both planar gold an on gold nanoparticles.

Liquid crystalline phases from polymer functionalised semiconducting nanorods
Matthias Zorn, Stefan Meuer, Muhammad Nawaz Tahir, Yuriy Khalavka, Carsten Soennichsen, Wolgang Tremel, Rudolf Zentel, Journal of Materials Chemistry 2008, 18, 3050-3058. DOI:10.1039/b802666a
Fig.: Newly designed block copolymers enable the functionalisation of various semiconducting anisotropic nanoobjects. They can thus be solved in various solvents and self-assembled into LC-phases at higher concentration.
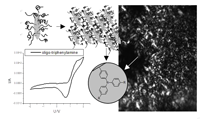
Liquid Crystalline Orientation of Semiconducting Nanorods in a Semiconducting Matrix
Matthias Zorn, Rudolf Zentel, Macromolecular Rapid Communication 2008, 29. 922-927.
DOI:10.1002/marc.200800165
Fig.: In this article we present the synthesis of block copolymers (RAFT-polymerization), which contain a semiconducting block and an anchor block, and which bind efficiently to formanisotropic semiconducting nano-rods from TiO2, SnO2 or ZnO. Thus stable dispersions of nanorod structures can be obtained in simple liquids and in a matrix of organic hole conducting materials. Concentrated dispersions of the nanorods in an oligomeric triarylamine matrix form phases with liquid crystalline behavior due to self-organization of the rod-like inorganic mesogens.
Columnar mesophases of hexabenzocoronene derivatives. I. Phase transitions
Valentina Marcon, Thorsten Vehoff, James Kirkpatrick, Cheol Jeong, Do Y. Yoon, Kurt Kremer, Denis Andrienko, The Journal of Chemical Physics 2008, 129, 094506. DOI:10.1063/1.2969764
Fig.: Using atomistic molecular dynamic simulations we study the transitions between solid herringbone and liquid crystalline hexagonal mesophases of discotic liquid crystals formed by hexabenzocoronene derivatives. Combining a united atom representation for the side chains with the fully atomistic description of the core, we study the effect of side chain substitution on the transition temperatures as well as molecular ordering in the mesophases. Our study rationalizes the differences in charge carrier mobilities in the herringbone and hexagonal mesophases, which is predominantly due to the better rotational register of the neighboring molecules.
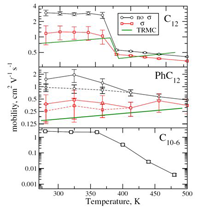
Columnar mesophases of hexabenzocoronene derivatives. II. Charge carrier mobility
James Kirkpatrick, Valentina Marcon, Kurt Kremer, Jenny Nelson, Denis Andrienko, The Journal of Chemical Physics 2008, 129, 094506. DOI:10.1063/1.2969764
Fig.: Combining atomistic molecular dynamic simulations, Marcus–Hush theory description of charge transport rates, and master equation description of charge dynamics, we correlate the temperature-driven change of the mesophase structure with the change of charge carrier mobilities in columnar phases of hexabenzocoronene derivatives. The time dependence of fluctuations in transfer integrals shows that static disorder is predominant in determining charge transport characteristics. We look at three mesophases of hexabenzocoronene: herringbone, discotic, and columnar disordered. All results are compared to time resolved microwave conductivity data and show excellent agreement with no fitting parameters.
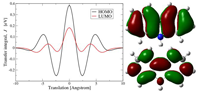
Atomistic force field and electronic properties of carbazole: from monomer to macrocycle
Thorsten Vehoff, James Kirkpatrick, Kurt Kremer, Denis Andrienko, Physica Status Solidi 2008, b, 1-5. DOI:10.1002/pssb.200743450
Fig.:
An atomistic force-field is developed for a carbazole monomer, oligomers, and alkyne-substituted polymers. This force-field is then used to study the morphology of stacks of carbazole macrocycles. Charge transport of macrocycles in columnar arrangement is analyzed using non-adiabatic high-temperature Marcus theory.
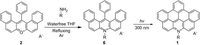
Synthesis and self-assembly of dibenzo[jk,mn]naphtho[2,1,8-fgh]thebenidinium derivates
Dongqing Wu, Xinliang Feng, Masayoshi Takase, Monika C. Haberecht, Klaus Müllen, Tetrahedron 2008, 64 (50), 11379-11386.
DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2008.08.063
A novel synthetic method toward nitrogen containing positively charged dibenzo[jk,mn]naphtho[2,1,8-fgh]thebenidinium (DBNT, 1) salts was developed. In this method, the undehydrogenated precursor of DBNT, 14-phenyl-14-dibenzo[a,j]acridinium salt (6), was produced directly from the reaction between 14-phenyl-14-dibenzo[a,j]xanthenylium (2) and amine/aniline in reasonable yield. Various DBNT salts with different alkyl and alkylphenyl chains were synthesized in this two-step method. The self-assembly behavior of two alkylated DBNT salts, 1c and 1f, was studied in this work. Due to the different substituents and counterions, compound 1c formed nanoscale wirelike fibers, and helical aggregates were obtained from 1f, in their methanolic solutions.
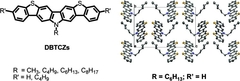
Conjugated Ladder-Type Heteroacenes Bearing Pyrrole and Thiophene Ring Units: Facile Synthesis and Characterization
Peng Gao, Xinliang Feng, Xiaoyin Yang, Volker Enkelmann, Martin Baumgarten and Klaus Müllen, J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73 (23), 9207–9213.
DOI: 10.1021/jo801898g
Ladder-type heteroacenes containing pyrrole and thiophene rings, dibenzo[b,b′]thieno[2,3-f:5,4-f′]-carbazoles (DBTCZ, 1), and diindolo[3,2-b:2′,3′-h]benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b′]bis[1]benzothiophene (DIBBBT, 2), were facilely synthesized through proper precursors (7, 11, and 18) respectively. The key step is a triflic acid induced intramolecular electrophilic coupling reaction of corresponding aromatic methyl sulfoxides with activated aromatic building blocks, which enables regioselective ring closure. Both precursors (7 and 11) toward DBTCZ gave the symmetrical product but with solubilizing alkyl chains in two different fashions. DIBBBT was also synthesized as the extended ladder-type heteroacene with defined structure. These obtained heteroacenes are fully characterized (mass spectrometry, NMR, elemental analysis), and their X-ray analysis and optical and electrochemical properties are reported.